Difference between revisions of "ISO26262/V-Cycle/5. Product development at the hardware level"
(Created page with "{{ISO26262}}") |
|||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{ISO26262}} | {{ISO26262}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:5.V-Cycle-Product_Development_HW_level.png]] | ||
| + | |||
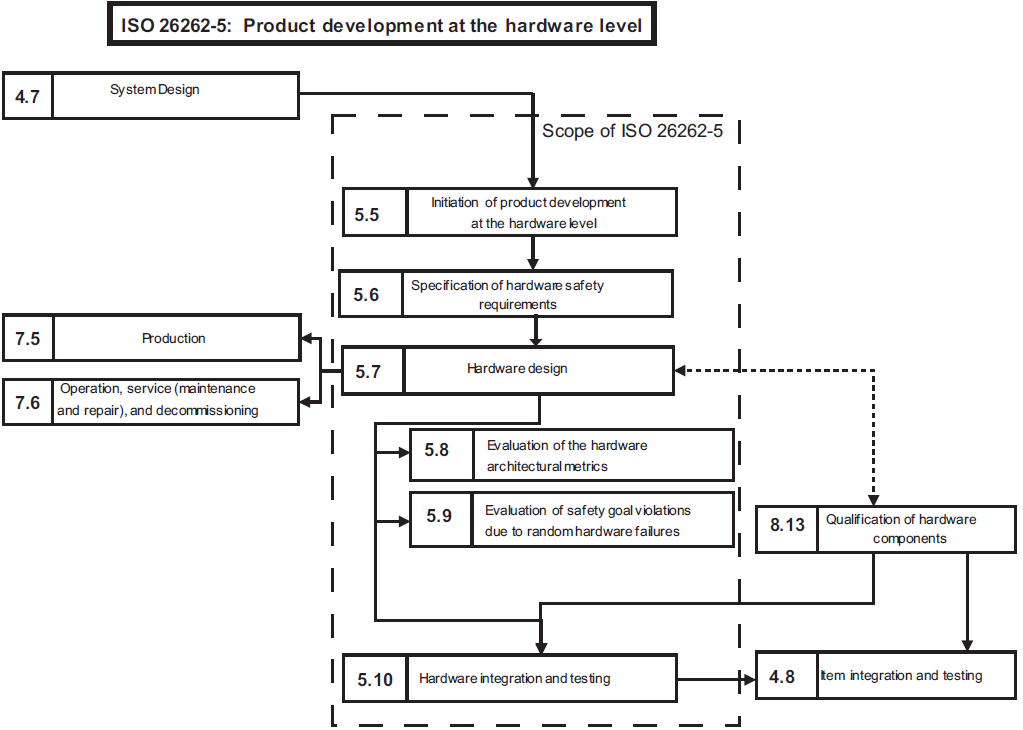
| + | During this phase the necessary activities and processes needed to develop safety critical hardware are planned. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''These activities and processes include:''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | * Hardware implementation of the technical safety concept | ||
| + | * Analysis of potentioal hardware faults and their effects | ||
| + | * Coordination with software development | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:5_SafetyLifecycle-Hardware_Detailed.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-5_Initiation_of_Product_Development_at_the_Hardware_Level|5-5 Initiation of Product Development at Hardware Level]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Planning of safety activities in hardware development | ||
| + | - Further refinement of the Safety Plan | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-6_Specification_of_Hardware_Safety_Requirements|5-6 Specification of Hardware Safety Requirements]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Derivation of hardware safety requirements from the technical safety concept and system design specification | ||
| + | - Specification of reliability requirements to be met by hardware | ||
| + | - Detailing of the hardware-Software Interface specification | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-7_Hardware_Design|5-7 Hardware Design]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Design the hardware in accordance with the system design specification and the hardware safety requirements | ||
| + | - Verify the hardware design against the system design specification and the hardware safety requirements | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-8_Evaluation_of_the_Hardware_Architectural_Metrics|5-8 Evaluation of the Hardware Architectural Metrics]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Evaluate the hardware architecture regarding the compliance to the safety requirements | ||
| + | - Single Point Fault Metrics (SPFM) | ||
| + | - Latent Fault Metric (LFM) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-9_Evaluation_of_the_Safety_Goal_violations_due_to_Random_Hardware_Failure|5-9 Evaluation of the Safety Goal Violations]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Prove that the risk of a safety goal violation, dus to random hardware failures, is sufficiently low (Use PMHF or Joe Miller method) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-10_Hardware_Integration_and_Testing|5-10 Hardware Integration and Testing]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Verification of the compliance of the developed hardware with the hardware safety requirements and hardware specification, by testing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <center> | ||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/4-11_Release_for_Production| Previous Chapter (4-11) | ]] | ||
| + | [[ISO26262/V-Cycle/5-5_Initiation_of_Product_Development_at_the_Hardware_Level|Next Chapter (5-5)]] | ||
| + | </center> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:27, 10 October 2017
During this phase the necessary activities and processes needed to develop safety critical hardware are planned.
These activities and processes include:
- Hardware implementation of the technical safety concept
- Analysis of potentioal hardware faults and their effects
- Coordination with software development
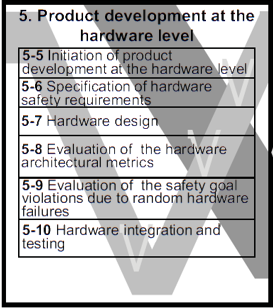
5-5 Initiation of Product Development at Hardware Level
- Planning of safety activities in hardware development - Further refinement of the Safety Plan
5-6 Specification of Hardware Safety Requirements
- Derivation of hardware safety requirements from the technical safety concept and system design specification - Specification of reliability requirements to be met by hardware - Detailing of the hardware-Software Interface specification
- Design the hardware in accordance with the system design specification and the hardware safety requirements - Verify the hardware design against the system design specification and the hardware safety requirements
5-8 Evaluation of the Hardware Architectural Metrics
- Evaluate the hardware architecture regarding the compliance to the safety requirements - Single Point Fault Metrics (SPFM) - Latent Fault Metric (LFM)
5-9 Evaluation of the Safety Goal Violations
- Prove that the risk of a safety goal violation, dus to random hardware failures, is sufficiently low (Use PMHF or Joe Miller method)
5-10 Hardware Integration and Testing
- Verification of the compliance of the developed hardware with the hardware safety requirements and hardware specification, by testing.